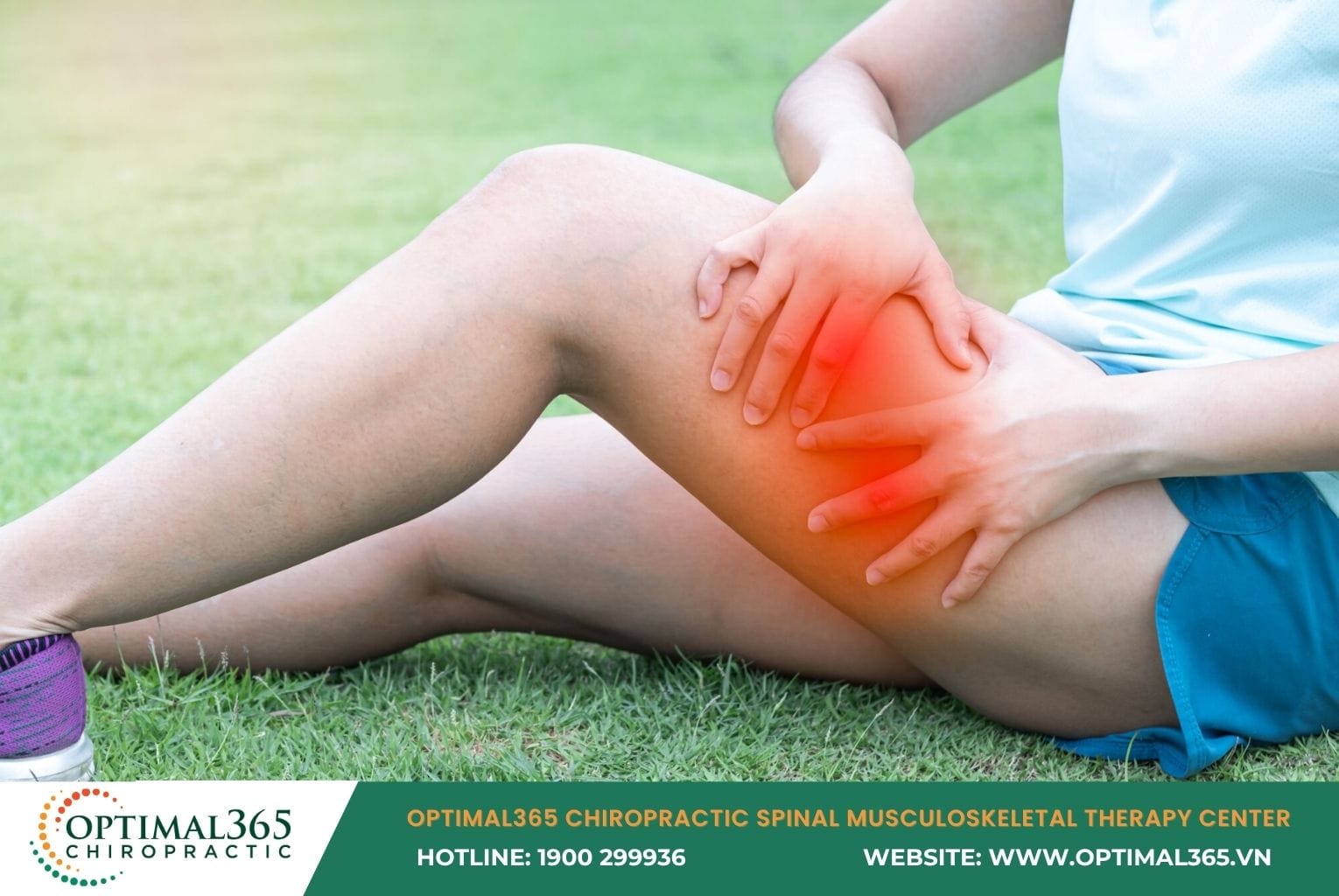
Thigh muscle strain is a common injury that causes pain and restricts movement if not detected early. Its symptoms are often obvious but easily overlooked. Understanding the causes and applying timely recovery solutions can help you reduce pain effectively, prevent complications, and maintain an active, healthy lifestyle.
What is Thigh Muscle Strain?
Thigh muscle strain occurs when the muscle fibers in the thigh area—including the quadriceps (front thigh muscles), hamstrings, adductors, and others—are overstretched, leading to micro-tears or mild rips. According to MedlinePlus, this is a frequent muscle injury in adults, especially during activities requiring high strength or flexibility without proper preparation.
Between ages 35 and 55, musculoskeletal elasticity and endurance begin to decline, leading to aches and stiffness. Beyond discomfort, thigh muscle strain can limit mobility, directly impacting work—particularly for office workers who sit for long periods or business owners constantly on the move meeting clients.
You might also be interested in: Knee Strain – Symptoms and Treatment for Athletes
Symptoms of Thigh Muscle Strain
Early recognition of thigh muscle strain allows for a proper treatment and rest plan, preventing escalation. Here are the common signs:
Aching pain and tightness in the thigh: You may feel heaviness or stiffness when trying to bend or straighten your leg. The pain can intensify over hours or even the next day due to micro-tears in the muscle fibers.
Difficulty moving: Everyday actions like climbing stairs, sitting down, standing up, or leg exercises (squats, lunges) become challenging. For sedentary office workers, the pain may become pronounced upon standing after prolonged sitting.
Cramps and muscle spasms: A tight, numb sensation in the thigh muscles, especially during sudden posture changes or intense activity. Cramps are more likely when muscles are fatigued, dehydrated, or low on electrolytes.
Swelling and bruising: In moderate to severe thigh strain cases, fluid buildup causes swelling with bruising. This signals more significant fiber damage, requiring rest and medical support if needed.
Persistent dull ache: Without adequate rest or with continued high-intensity exercise, the pain can become chronic. Ignoring it increases the risk of full muscle tears or worsened injury.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical help if:
- Pain lasts over a week without improvement despite stopping intense activity.
- Large bruising, significant swelling, or complete loss of thigh flexion/extension/movement occurs.
- You hear a “pop” or “snap” during the injury, suspecting a severe tear.
These are red flags for serious muscle damage, requiring imaging diagnostics and tailored treatment.
Causes of Thigh Muscle Strain
Overexertion or Poor Posture
High-intensity sports like running, tennis, badminton, or soccer without thorough warm-ups force thigh muscles to overwork. Incorrect form in exercises (squats, lunges, deadlifts) or lifting weights beyond capacity heightens fiber strain risk.
Sedentary Lifestyle and Weak Muscles
Office workers or business owners sitting for hours weaken thigh muscles, reducing flexibility. Sudden physical demands catch unprepared muscles, leading to overstretching.
Sudden Movements
Quick standing, sitting, twisting, or abrupt direction changes in running apply intense pressure on thigh muscles. Those who’ve been seated long before sprinting or heavy lifting are particularly vulnerable as muscles can’t adapt instantly.
Prolonged Stress
Sleep deprivation and work pressure elevate cortisol, keeping muscles tense. Fatigued thigh muscles are prone to tears during strong or improper movements.
Dehydration or Nutrient Deficiencies
Muscles need water, vitamins, and minerals (calcium, magnesium) for elasticity. Poor protein intake or imbalanced nutrition weakens thigh muscles, increasing injury susceptibility.
Underlying Musculoskeletal Conditions
Knee osteoarthritis, tendonitis, or lumbar disc herniation can cascade to thigh muscles. Those over 40 with prior joint or spine injuries lose flexibility, making thigh strain more likely with faulty movements.
Degrees of Thigh Muscle Strain and Potential Complications
Mild (Grade I)
Symptoms: Mild aching and slight tightness in the affected thigh area.
Signs: Minimal or no swelling, no obvious bruising.
Recovery: Most cases self-resolve in 5–7 days with rest and RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) support.
Moderate (Grade II)
Symptoms: Sharper pain, mild swelling, and bruising around the thigh.
Signs: Noticeable impact on mobility, hindering daily activities.
Recovery: 2–4 weeks, often combining physical therapy for better outcomes.
Severe (Grade III)
Symptoms: Multiple or complete fiber tears causing intense pain, major swelling, and extensive bruising.
Signs: Severe mobility restriction, disrupting daily life and work.
Recovery: Over a month, needing advanced medical intervention; surgery may be required in some cases.
Untreated thigh muscle strain can lead to chronic pain or long-term gait and mobility issues.
Effective Treatments for Thigh Muscle Strain
RICE Method (Rest – Ice – Compression – Elevation)
This initial approach effectively reduces swelling, pain, and speeds recovery for thigh muscle strain, recommended by experts within 48 hours post-injury.
Rest – Limit activity to avoid worsening damage
Stop vigorous exercises like running, soccer, squats, or stair climbing. Use crutches if pain is severe to offload thigh pressure.
Note: Rest doesn’t mean total immobility. After 48 hours, if pain eases, incorporate gentle movements to prevent joint stiffness.
Ice – Reduce swelling and pain
Apply ice packs wrapped in cloth or gel packs to the sore area. 15–20 minutes per session, 3–4 times daily, especially first 48 hours. Avoid direct skin contact to prevent frostbite; use thin towels.
Note: Limit to 20 minutes/session to avoid impairing blood flow and recovery.
Compression – Minimize swelling and stabilize
Wrap elastic bandages around the thigh snugly but not tightly. Check every 1–2 hours: Loosen if numb, cold, or discolored. Avoid loose wrapping for ineffective fixation.
Note: Persistent swelling after 48 hours? Consult a doctor for assessment.
Elevation – Aid swelling and blood pooling reduction
When lying or sitting, elevate the leg above heart level with pillows. This improves circulation, curbing fluid buildup. Pair with ice for bruising or heavy swelling.
Note: Adjust height for comfort if numbness or sharp pain arises.
Advanced Physical Therapy with Cutting-Edge Technology
Tech-enhanced therapies stimulate blood flow, reduce inflammation, and alleviate thigh muscle strain pain quickly, using devices like:
Shockwave Therapy: High-intensity sound waves promote self-healing, ideal for chronic or recurrent strains.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Deep-tissue penetration reduces inflammation and boosts cell regeneration, widely used for musculoskeletal injuries.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises for Thigh Muscles
Stretching and strengthening are key for swift recovery and preventing thigh strain recurrence.
Quadriceps Stretch
Stand balanced against a wall or chair. Bend one leg back, grasp the ankle, and gently pull toward the glutes. Hold 15–30 seconds, repeat 3–5 times per side.
Hamstring Stretch
Sit on the floor, extend one leg, bend the other with sole against the thigh. Lean forward to touch toes without forcing. Hold 15–30 seconds, 3–5 reps per side.
Leg Extensions for Thigh Strength
Sit straight-backed, slowly extend one leg forward then lower. 10–15 reps per leg, 2–3 sets.
Note: Start light, progress gradually. Stop if sharp pain or cramps occur; seek expert advice.
Chiropractic Care
Per the American Chiropractic Association, chiropractic enhances muscle flexibility, corrects posture, and bolsters the musculoskeletal system.
Benefits of Chiropractic for Thigh Muscle Strain
Personalized Treatment Plans: Experts assess individual musculoskeletal states for tailored sessions. Perfect for busy office workers, entrepreneurs, or travelers needing non-invasive, efficient care.
Rapid Pain Relief and Long-Term Recovery: Reduces spinal, hip, and thigh pressure, easing adjacent muscle tension. Combined with PT, it outperforms standard exercises alone.
Preventing Recurrence: Proper alignment lowers re-injury risk, improving posture and curbing faulty movement habits stressing thigh muscles.
Frequently Asked Questions About Thigh Muscle Strain
How long does thigh muscle strain take to heal?
Depends on severity: Mild (5–7 days), moderate (2–4 weeks), severe (over 1 month). Shorten with rest, RICE, PT, or chiropractic.
Should you massage immediately after thigh strain?
Prioritize ice and rest first 48 hours. Then, light massage aids circulation and eases tightness.
What sports can middle-aged people do to avoid thigh strain?
Gentle options: Walking, swimming, cycling, yoga. Gradually increase intensity, warm up fully, avoid sudden overexertion.
Can thigh pain signal other conditions?
Possibly tendonitis, knee arthritis, or lumbar herniation. If persistent with numbness or swelling, see a doctor.
Specialized Thigh Muscle Strain Therapy Services at Optimal365 Chiropractic
At Optimal365 Chiropractic, clients access comprehensive thigh muscle strain treatments with these benefits:
Chiropractic Packages: Spinal and joint adjustments reduce thigh pressure, preventing recurrence.
Advanced Physical Therapy: High-tech devices plus targeted rehab for moderate/severe cases.
Customized Protocols: Thorough evaluations yield time-efficient, effective plans.
Promotions: 50% off initial consultations for new clients.
Learn more: Musculoskeletal and Spinal Disorders: Comprehensive Treatment Solutions at Optimal365 Chiropractic
Conclusion
Thigh muscle strain may seem minor but can significantly impact quality of life, especially for busy professionals or sports enthusiasts. To prevent and resolve it fully, grasp the causes, prioritize expert musculoskeletal care, and adopt fitting preventive measures for lasting relief and vitality.
Sources:
Mayo Clinic – Physical Therapy for Muscle Strains: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lichen-sclerosus/symptoms-causes/syc-20374448
Harvard Medical School – Stretching Exercises for Injury Recovery: https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-importance-of-stretching