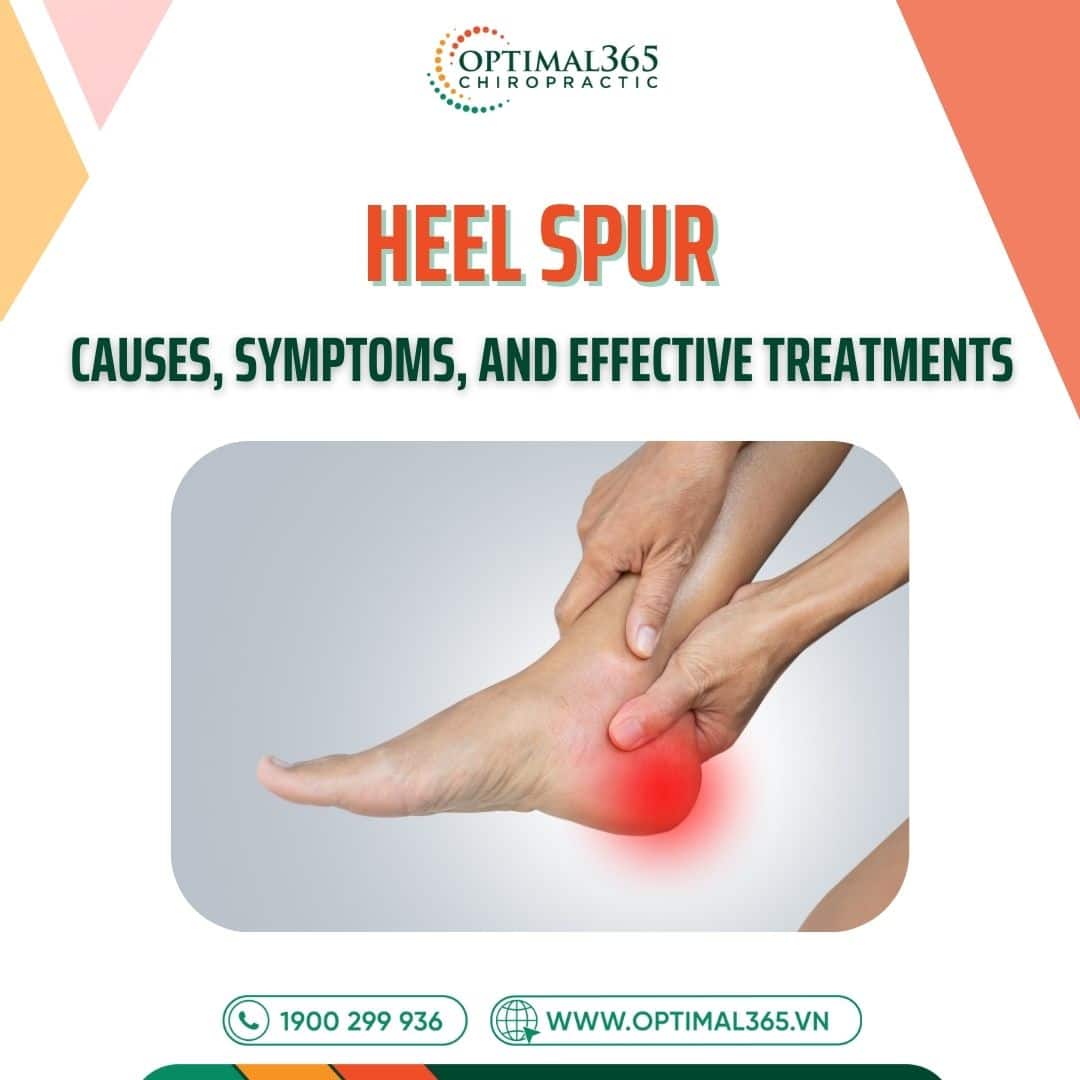
Heel spur is a common orthopedic condition that causes persistent or sharp pain in the heel, significantly affecting mobility and quality of life. If left untreated, it can become chronic and lead to complicated issues. This article provides comprehensive insights into heel spurs, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies to help you better understand and manage this condition effectively.
What is a Heel Spur?
A heel spur, also known as a calcaneal spur, is a small bony protrusion that forms at the heel due to prolonged calcium deposits at the attachment point of the plantar fascia. While heel spurs don’t always cause pain, discomfort becomes noticeable when inflammation occurs. This condition is common among older adults, athletes who put excessive stress on their feet, or individuals with jobs requiring prolonged standing, such as teachers or retail workers. Additionally, obesity and wearing improper footwear are significant risk factors. If untreated, heel spurs can lead to chronic heel pain, restricted movement, and other orthopedic complications.

What is a heel spur?
Causes of Heel Spurs
Heel spurs develop due to various factors, but the primary cause is the accumulation of calcium deposits in the heel bone. This occurs when soft tissues in the heel are subjected to prolonged irritation or injury, leading to the formation of bony growths. Key causes include:
- Repetitive Strain: Activities like running, jumping, or standing for long periods create continuous pressure on the heel, triggering spur formation.
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases stress on the feet, particularly the heels, raising the risk of heel spurs.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes without proper arch support or with hard soles can damage soft tissues in the heel.
- Related Conditions: Conditions like plantar fasciitis or rheumatoid arthritis may contribute to heel spur development.
Understanding these risk factors empowers you to take proactive steps for heel spur prevention and timely treatment.
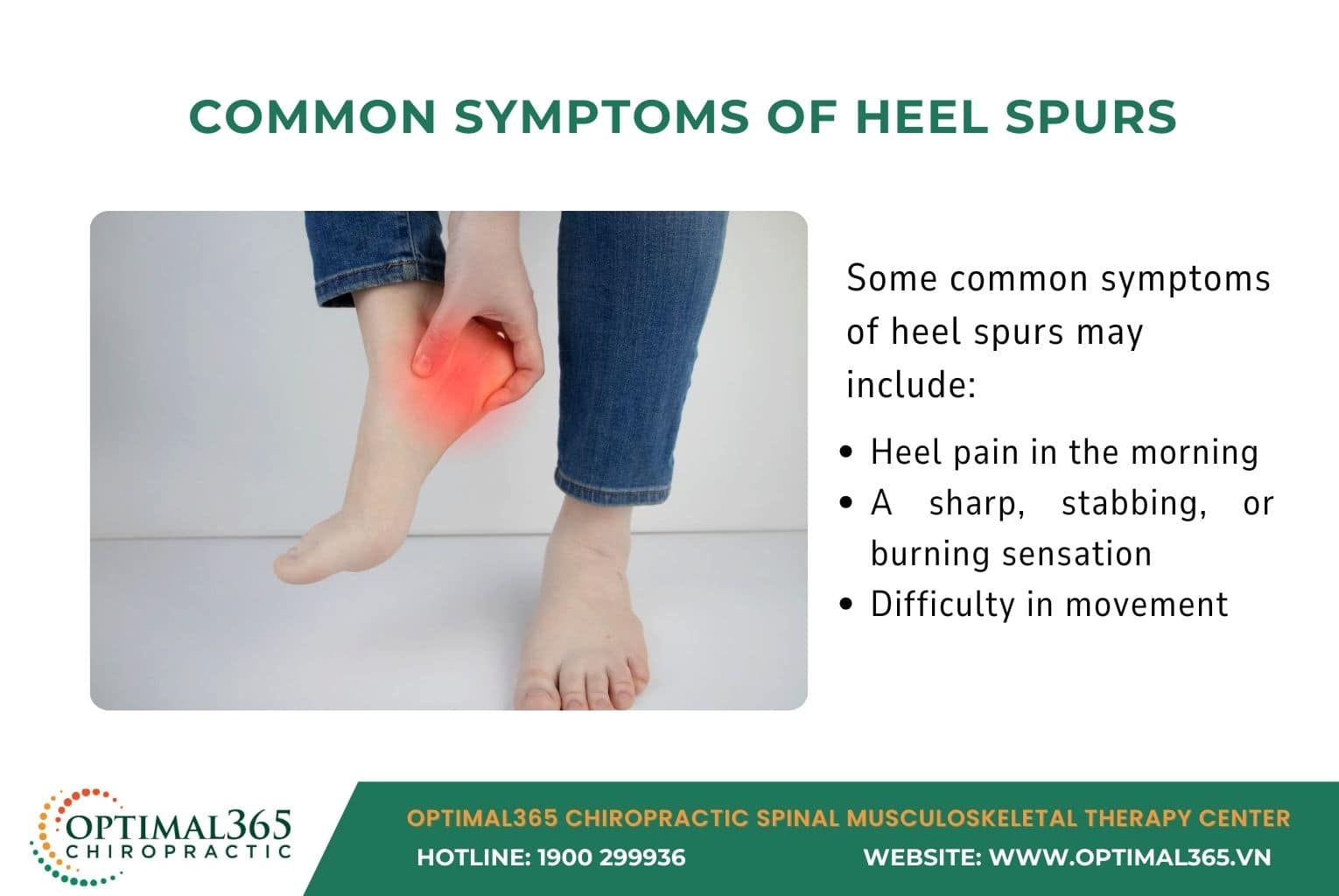
Common Symptoms of Heel Spurs
Individuals with heel spurs often experience sharp pain when taking their first steps in the morning, which may subside but recur with extended walking or standing. Some report a burning or tingling sensation in the heel, especially after prolonged activity. Persistent pain can make walking, running, or even standing challenging. Specific symptoms include:
- Morning Heel Pain: Intense pain when stepping out of bed, often referred to as “first-step pain.”
- Burning or Tingling Sensation: Discomfort like pins and needles or a burning feeling in the heel after standing or walking for long periods.
- Mobility Challenges: Prolonged heel pain can hinder daily activities like walking or running.
These symptoms may worsen without early intervention, impacting daily life and work performance.
Common Symptoms of Heel Spurs
Are Heel Spurs Dangerous?
While heel spurs are not life-threatening, they can significantly impair quality of life. Persistent pain may limit mobility, reduce work efficiency, and create challenges in daily activities. If left untreated, heel spurs can lead to complications such as:
- Chronic Joint Inflammation: Prolonged heel spurs may cause inflammation in nearby joints, such as the ankle.
- Reduced Mobility: Chronic pain can discourage movement, leading to muscle weakness or joint stiffness.
- Foot Deformities: In rare cases, untreated heel spurs may alter the foot’s structure.
Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent these complications and maintain optimal mobility.
Diagnosing Heel Spurs
Diagnosing heel spurs involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging tests. The process typically includes:
- Clinical Examination: A doctor will assess symptoms, medical history, and examine the heel for pain and mobility issues.
- X-ray Imaging: X-rays are commonly used to detect heel spurs and evaluate their severity.
- Differential Diagnosis: Symptoms of heel spurs resemble those of plantar fasciitis, ankle arthritis, or stress fractures. Doctors use imaging and symptoms to confirm the diagnosis.
Accurate diagnosis forms the foundation for an effective heel spur treatment plan tailored to each patient.
Diagnosing Heel Spurs
Heel Spur Treatment Options
Heel spur treatment is divided into non-surgical and surgical approaches, depending on the condition’s severity.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Most heel spur cases can be managed effectively without surgery. Common non-surgical treatments include:
- Rest: Limiting activities that stress the heel, such as prolonged standing or running, helps reduce inflammation and pain.
- Cold Compress and Physical Therapy: Applying cold packs reduces swelling, while physical therapy exercises improve foot flexibility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can alleviate symptoms.
- Supportive Footwear: Wearing shoes with soft soles, arch support, or custom orthotics reduces pressure on the heel.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be considered if conservative treatments fail. The procedure involves removing the spur and relieving inflamed tissues. However, surgery carries risks like infection or prolonged recovery. Post-surgery, patients must follow rehabilitation guidelines for optimal recovery.
Preventing Heel Spurs
Preventing heel spurs is the best way to avoid the discomfort they cause. Effective heel spur prevention strategies include:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess weight minimizes stress on the feet.
- Choose Proper Footwear: Opt for shoes with soft soles, good arch support, and a proper fit.
- Exercise Correctly: Avoid high-impact activities that strain the heels and warm up properly before physical activity.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Strengthen calf and foot muscles through targeted exercises to reduce injury risk.
These habits not only prevent heel spurs but also promote overall orthopedic health.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor if you experience the following:
- Heel pain lasting more than a few weeks despite rest.
- Severe pain affecting sleep or daily activities.
- No improvement from home remedies like cold compresses or pain relievers.
Early consultation ensures accurate diagnosis and prevents long-term complications.
Heel spurs are a common orthopedic issue, but with early detection, they can be effectively managed and treated. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and prevention strategies, you can reduce your risk and improve your quality of life. Don’t let heel pain hold you back. Every day of delay can worsen the condition. Take charge of your orthopedic health-schedule a consultation at Optimal365 Chiropractic for expert advice and a personalized heel spur treatment plan.