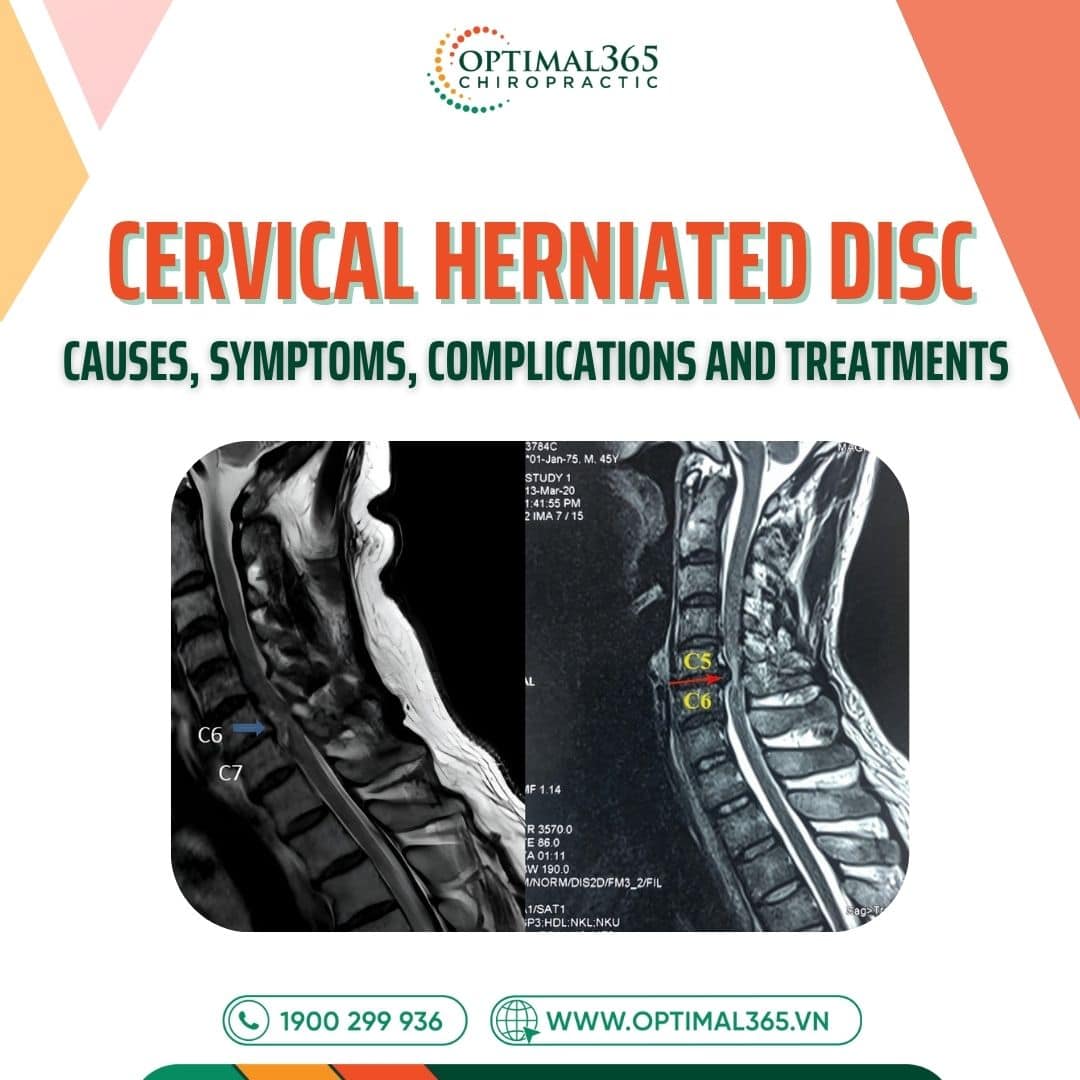
Cervical herniated disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus escapes its normal position, compressing nerve roots or the spinal cord, leading to pain, tingling, and weakness. If left untreated seriously, the condition can worsen, even causing permanent paralysis. So, what are the causes, symptoms, complications, and treatments for cervical herniated disc? Let’s explore in detail with Optimal365 Chiropractic in this article.
Structure of Cervical Spine and What is Cervical Herniated Disc?
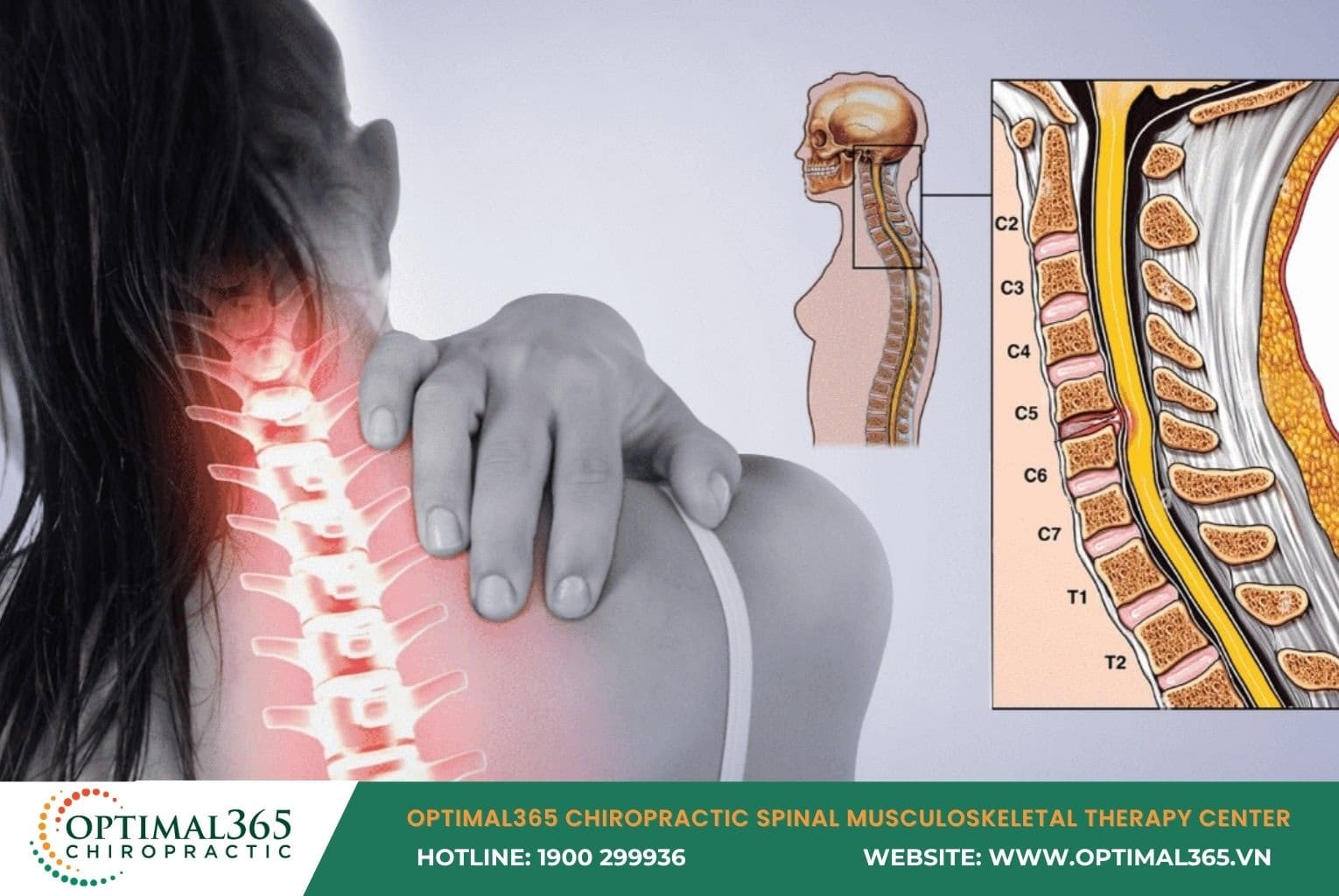
The cervical spine consists of 7 vertebrae: C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, connected by intervertebral discs, slightly curved in a C-shape. Each disc acts like a “rubber cushion” with a jelly-like nucleus pulposus in the center and a fibrous annulus outside, absorbing shocks and enabling spinal flexibility.
Inside the disc, the nucleus pulposus (gel-like structure) contains proteoglycans, surrounded by a circular fibrous annulus mainly made of collagen fibers. Finally, endplates between the cartilage and vertebral body protect the surface, preventing the nucleus from being compressed inward.
Cervical herniated disc happens when the disc ages, tears, or suffers trauma. At this point, the nucleus pulposus protrudes from the annulus, compressing nerve roots or the spinal cord, causing pain and various symptoms.
Cases with multiple discs herniating simultaneously lead to multi-level cervical herniated disc, with higher complication risks. Here, pressure on the spine is much greater than in single-level herniation.
Cervical herniated disc and lumbar issues often affect those over 40. The cervical area occurs earlier due to poorer nerve and blood vessel supply, leading to early degeneration. According to research from Hoa Binh Provincial General Hospital (Hoa Binh Department of Health), cervical herniated disc is common, with an estimated incidence of about 18.6/100,000 people.
Causes of Cervical Herniated Disc
Aging
Over time, the spine loses its inherent flexibility. In some cases, discs weaken due to natural human aging. Discs gradually lose water, becoming thinner and impacting shock absorption. Thus, discs in older adults are more prone to injury. However, as warned by musculoskeletal specialists at University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City, this condition is increasingly affecting younger people, especially office workers.
Genetics
Statistics show genetically influenced cervical herniated disc accounts for only about 10%. Genes affect disc structure or the body’s response to factors like age or trauma. People with parents or siblings having herniated discs face higher risks than those without family history. For these cases, pay special attention to daily movement and lifestyle habits, limit caffeine, alcohol, and unhealthy foods. Regular spine check-ups and screenings at reputable chiropractic centers are suitable to minimize disease progression.
Unhealthy Lifestyle
An unhealthy lifestyle is a primary cause of cervical herniated disc and worsens the condition. This includes sedentary habits, weakening muscles around the neck and failing to support spinal pressure reduction. Additionally, diets lacking joint nutrients (calcium, chondroitin, glucosamine…), smoking, and alcohol quickly degrade disc quality.
Incorrect Postures in Daily Activities
Poor sitting posture, improper heavy lifting, sudden twisting or neck rotation… all relate to daily postures leading to cervical herniated disc. As shared in Health & Life newspaper (Ministry of Health’s organ), MSc. Dr. Nguyen Huy Hoang recommends correcting wrong postures like hunched sitting, bent standing, excessive arching, prolonged standing in one position, or prone sleeping.
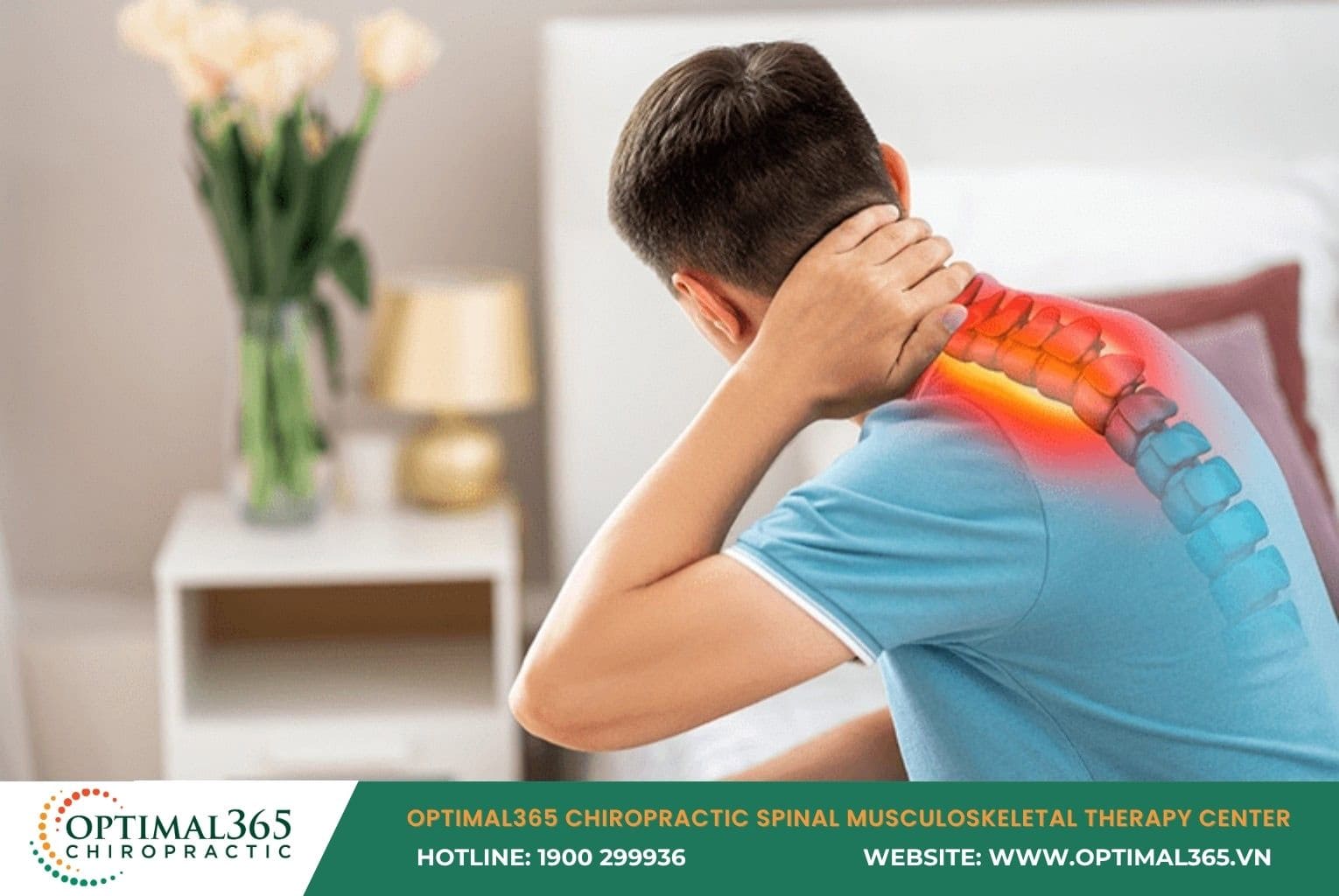

Symptoms of Cervical Herniated Disc
Clinical Signs of Cervical Herniated Disc
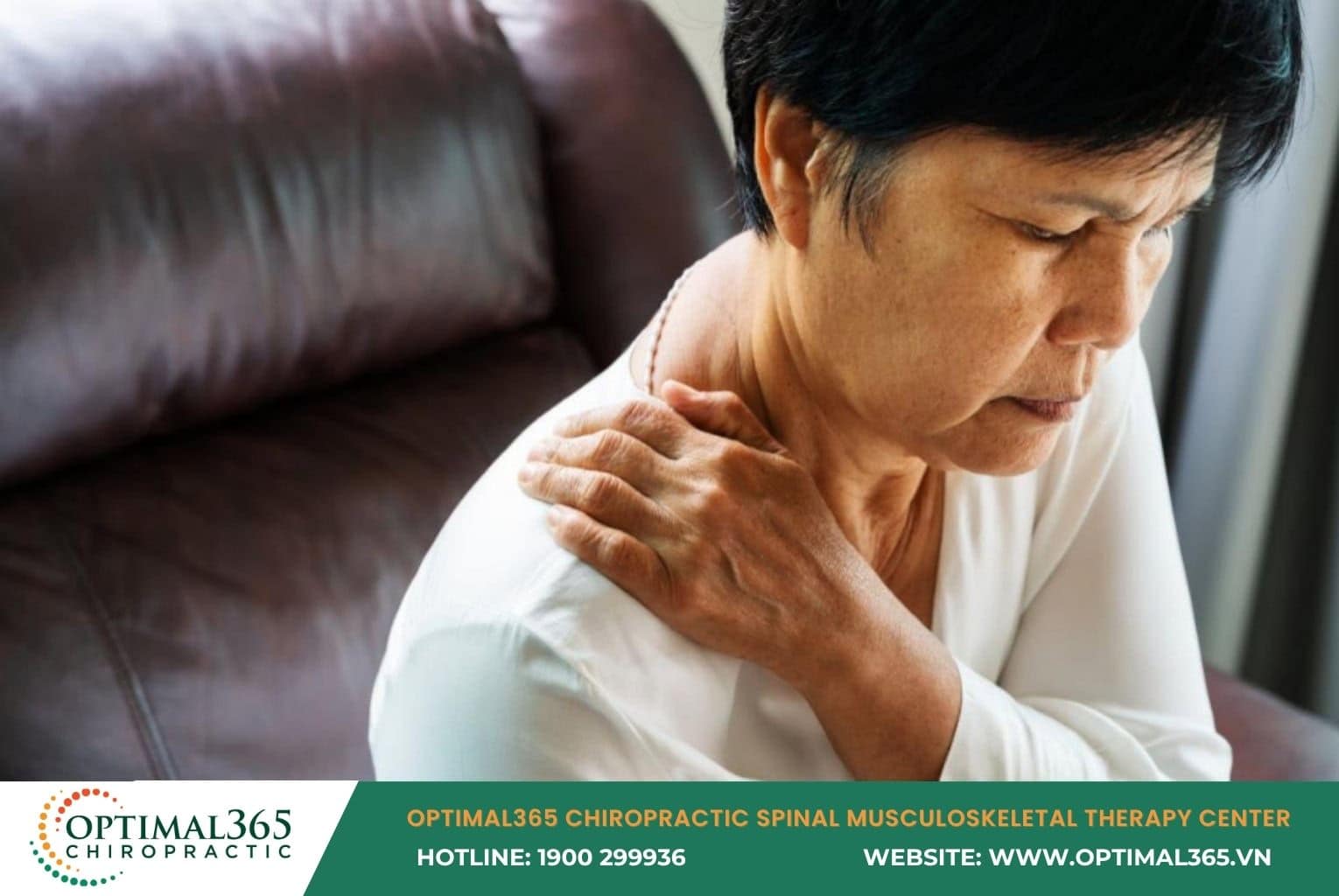
Cervical herniated disc often causes clear clinical symptoms. Initially, patients feel pain in 1-2 cervical vertebrae, then spreading to shoulders, arms, back of head, and eye sockets. Tingling may appear from the neck spreading body-wide or focused on arms, hands, and fingers.
Patients also struggle with bending, extending, or rotating the head, feeling uncomfortable during actions like reaching behind the back or raising arms high. Other signs include difficulty breathing, one-sided chest pain, pain when coughing, sneezing, or defecating.
Subclinical Signs of Cervical Herniated Disc
In subclinical cases, cervical herniated disc symptoms are detected via MRI showing: Disc herniating anteriorly or posteriorly, nucleus pulposus displaced, spinal structure changes, and compression on nerve roots or spinal cord.
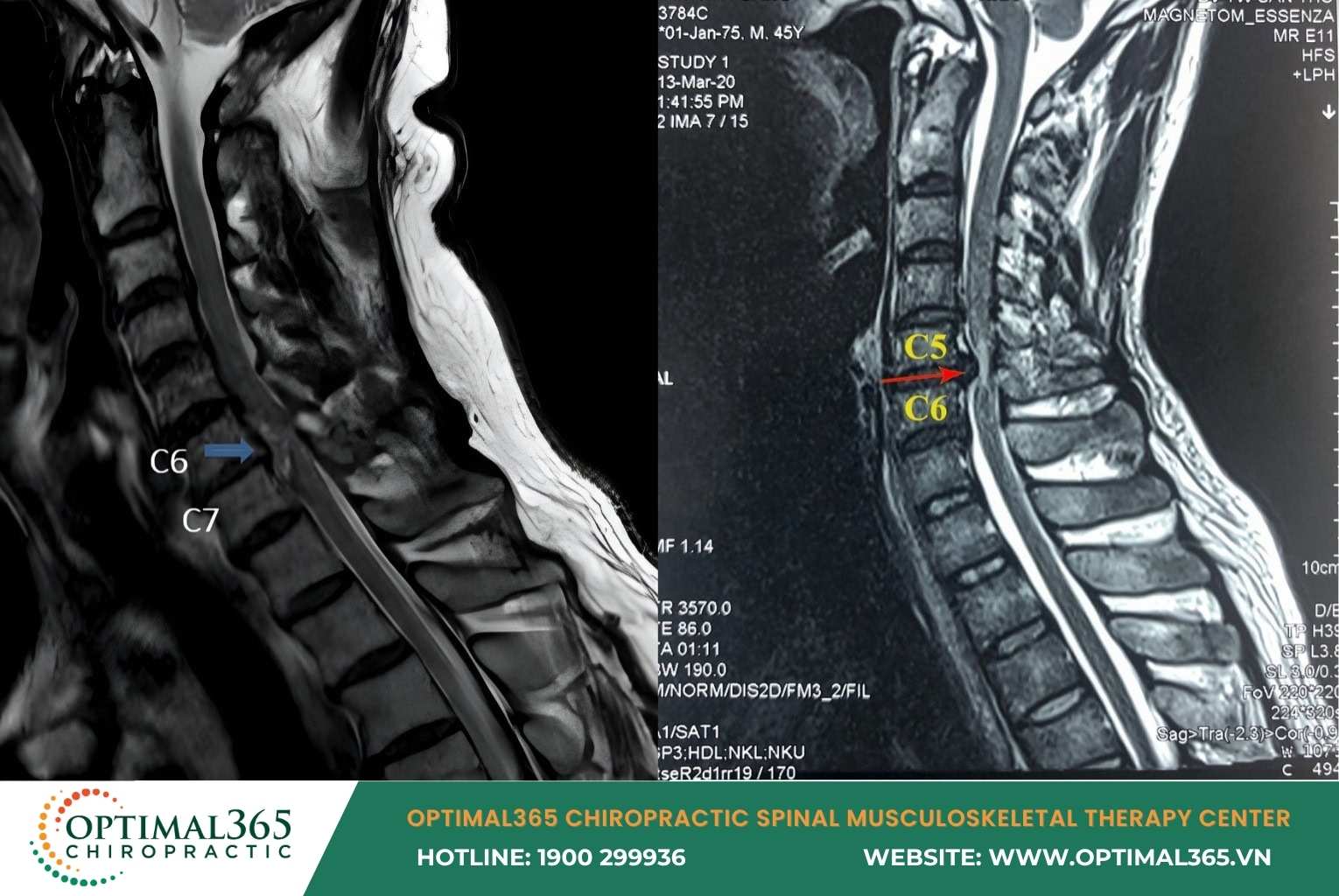
Symptoms of Cervical Herniated Disc Progressing by Severity Levels
Cervical herniated disc symptoms can increase by levels:
- Level 1: Slight neck stiffness and pain when bending or extending the head, pain spreading to shoulders and worsening with heavy work.
- Level 2: Prolonged pain from nape to back of head and ears, pain even with slight neck rotation.
- Level 3: Ache in occipital, forehead, nape areas spreading to shoulders, with numbness in one or both arms, sometimes hiccups, yawning, tearing, and dizziness during activity.
These symptoms need early recognition for timely treatment, reducing complication risks and improving life quality.
Dangerous Complications from Cervical Herniated Disc
Cerebral Ischemia
Cervical herniated disc causing cerebral ischemia stems from disc degeneration forming bone spurs. These spurs and escaped nucleus compress arteries, leading to unstable brain blood flow. Patients often experience headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, nausea. More severely, it can cause strokes, cerebral hemorrhage, memory decline.
Dangerous dizziness caused by reduced blood flow to the brain
Cervical Spinal Stenosis
According to Military Medical Journal issue 3-2019, herniated discs are the most common cause of spinal stenosis. Each spinal canal contains discs that cushion the spine. When herniated, abnormally bulging discs alter structure, reducing canal diameter, pressuring the canal, narrowing space for spinal cord and nerves. Patients feel shoulder-neck fatigue, numbness, and limb weakness. This intensifies with prolonged straight posture and eases when relaxing lying down.
Spinal Cord Compression
A common complication of cervical herniated disc. Specifically, complete annulus tear allows nucleus escape, compressing nerve roots and spinal foramen. Results include intense pain, loss of sensation in limbs, numbness, arm cramps, one-sided chest pain, movement difficulty, trouble lifting arms. When severe, risks include arm muscle atrophy, neurological disorders, even disability.
Permanent Paralysis
Permanent paralysis is the most serious complication of cervical herniated disc. Spinal cord pressure damages nerves, leading to lost mobility. Daily activities become difficult or completely impossible in limbs without timely intervention.
Numbness and Brachial Plexus Nerve Damage
Cervical nerves (cervical roots) extend from spinal cord through intervertebral foramina, spreading body-wide including arms. Herniation compresses these roots, causing pain, numbness, weakness, or pin-prick sensations down arms.
Manifestations include dull then sharp pain in neck, shoulders spreading to arms. Without posture change, movement, or strong neck muscle actions, pain prolongs and worsens.
Autonomic Nervous System Disorder
Autonomic disorder from cervical herniated disc occurs when nerves or spinal cord compression affects automatic nervous system function. This leads to indigestion, digestive disorders, uneven cold/hot sensations, sudden blood pressure changes.
Clear signs include dizziness, tinnitus, imbalance, eye socket pain, intermittent blurred vision. Additionally, sudden facial flushing, sweating, low blood pressure, increased bowel motility, chest pain from esophageal compression causing swallowing difficulty.
Widespread Body Pain
Pain starts in the neck, spreading to shoulders, arms, then from cervical to lumbar spine, down buttocks, thighs, legs. Patients feel aching, dull pain or pin-pricks, with numbness or muscle weakness in limbs.
Treatments for Cervical Herniated Disc
Cervical herniated disc is dangerous, impacting patient life quality. Treatment must be systematic, suited to each stage and specific condition.
Medical Treatment
Non-invasive method for mild to moderate cervical herniated disc. Common medical treatments include drugs like:
- Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories (ibuprofen, naproxen, corticosteroids): Reduce pain, swelling.
- Muscle relaxants (gabapentin, pregabalin): Relax spasmed muscles, reduce stiffness.
- Nerve supplements: Improve numbness, tingling.
Additionally, acupuncture, acupressure, physical therapy, supportive devices, and lifestyle adjustments.
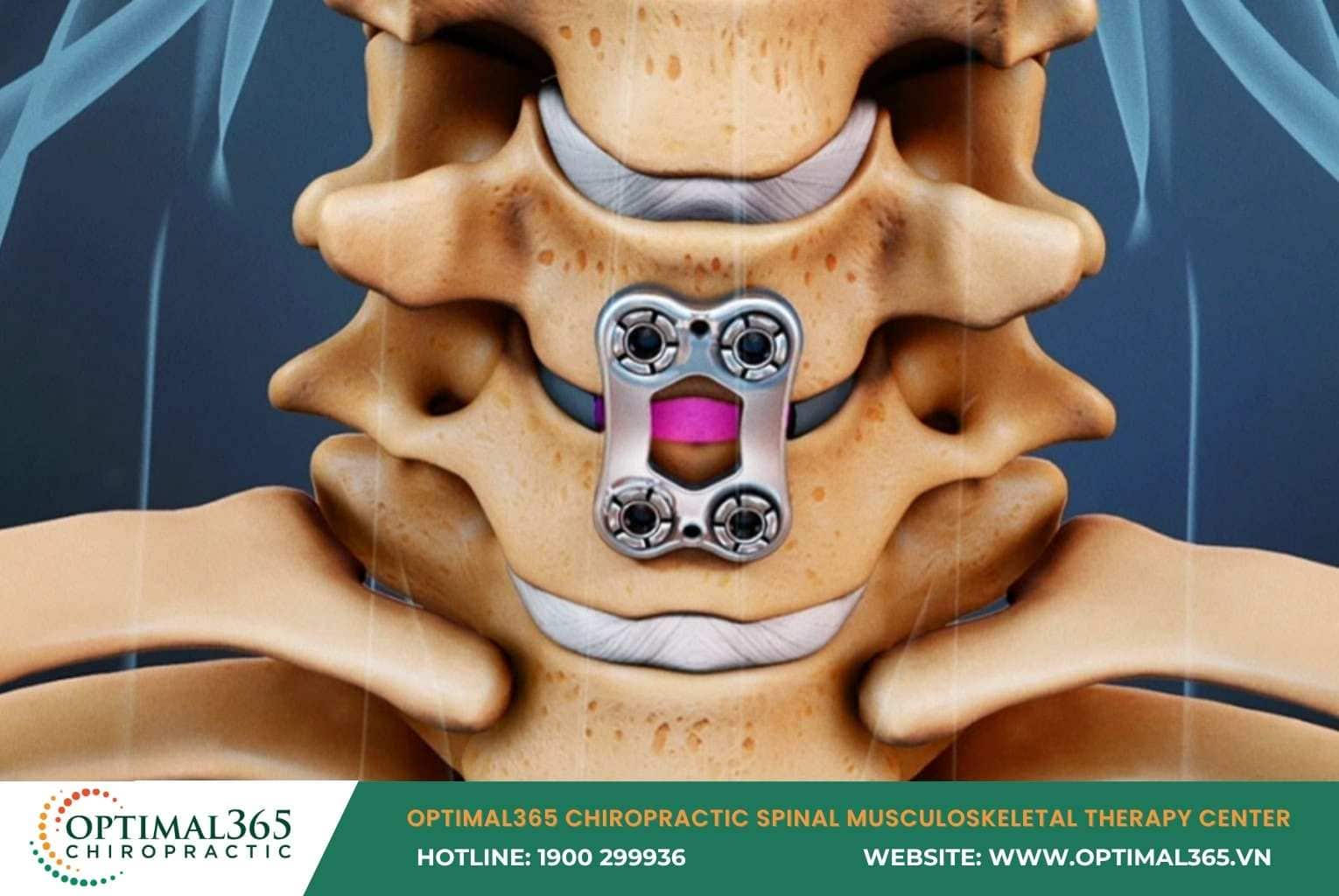
Surgery
Per UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines, surgery considers only after conservative treatments fail for 6-8 weeks. NICE estimates only 5% need surgery when:
- Prior treatments ineffective
- Herniation causes cauda equina syndrome, leg paralysis, bladder disorders, uncontrolled urination/defecation, perianal/genital numbness.
- Stomach ulcers, organ damage from excessive painkiller abuse
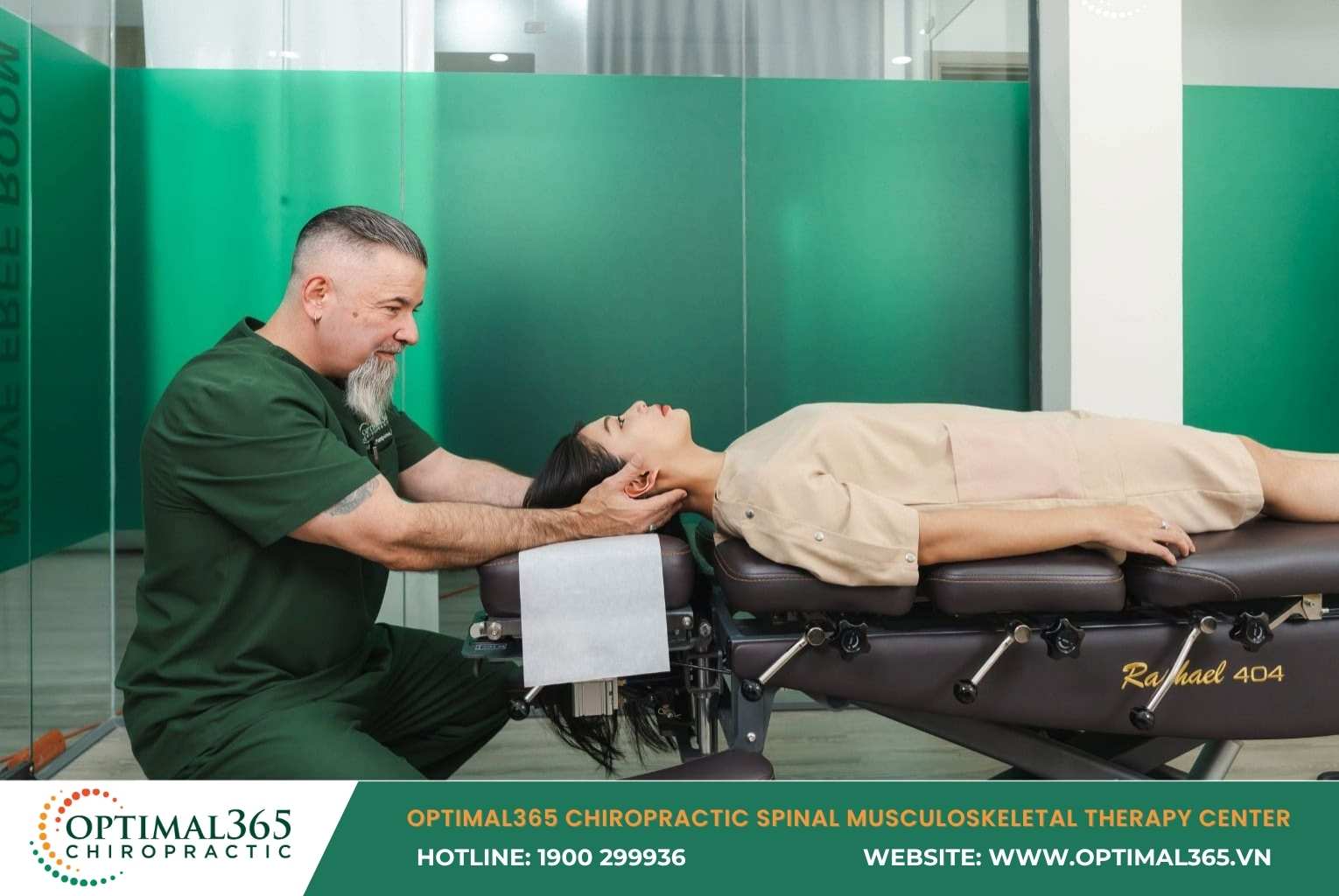
Chiropractic Spinal Therapy
Chiropractic is evaluated as optimal non-surgical treatment for cervical herniated disc, effectively pushing back pain and significantly improving movement. Main techniques adjust vertebrae and disc positions via:
- Professional spinal manipulation.
- Specialized decompression equipment.
- Rehabilitation exercises under expert guidance.
Treating Cervical Herniated Disc at Optimal365 Chiropractic Center
Instead of temporary pain-blocking drugs, Optimal365 Chiropractic advises seeking solutions from experienced Chiropractic specialists in spinal manipulation for examination and treatment. Though new in Vietnam, Chiropractic has developed over 125 years in developed countries like the US. It’s a safe conservative method: non-surgical, non-invasive, optimal recovery for musculoskeletal and spinal issues.
Per International Chiropractic Association research: Serious complication rates in Chiropractic are rare, under 1 in 1 million treatments. They emphasize it’s among the safest non-invasive therapies for spine problems, including cervical herniated disc.
Technically, doctors precisely identify herniation points, manually manipulate pain-causing spots to restore disc position. This releases disc compression on nerves and spinal cord. Adjusted vertebrae reduce pressure on discs, restoring function and restructuring them.
Optimal365 Chiropractic is successfully applying Chiropractic manipulation to address root causes of cervical herniated disc, spinal degeneration, scoliosis, sciatica… Restoring balance and flexibility. Patients can trust dedicated specialist support, modern equipment, effective therapies.
At Optimal365 Chiropractic in Vietnam, patients receive international-standard care at much better prices than overseas treatments.
Prevention Methods for Cervical Herniated Disc
To prevent cervical herniated disc, eliminating causes is essential. Adjust postures correctly in daily activities, especially work, sitting, heavy lifting. When lifting, squat first then stand slowly, avoid bending to lift.
Proper exercise plays a key role in prevention. Choose suitable sports; swimming or yoga are excellent for this condition.
With experienced doctors and experts, modern equipment, Optimal365 Chiropractic commits to dedicated care, close monitoring of cervical herniated disc treatment for optimal results. Visit Optimal365 Chiropractic for examination and best protocol treatment.
Reference source:
1. Staehler, R. (n.d.). Cervical herniated disc symptoms and treatment options. Spine-health. https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/herniated-disc/cervical-herniated-disc-symptoms-and-treatment-options
2. Mayo Clinic. (2023, October 24). Herniated disk – Diagnosis and treatment. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354101
3. UF Health. (n.d.). Cervical herniated disk. https://ufhealth.org/conditions-and-treatments/cervical-herniated-disk
4. Medtronic. (n.d.). Treatment options for cervical herniated disc. https://www.medtronic.com/uk-en/patients/treatments-therapies/cervical-herniated-disc-artificial/treatment.html